|
CV | Google Scholar | GitHub | Twitter | LinkedIn I recently completed my PhD at the Graphics and Imaging Laboratory at the University of Washington, Seattle, where I worked with Prof. Linda Shapiro and Prof. Ranjay Krishna. My research, situated at the intersection of vision and language, spans areas such as visual instruction tuning, self-supervised learning, and diffusion models. My work was supported by the Fulbright Fellowship (2019-2021), the Garvey Institute (2021-2022) and Microsoft (2023-2024). I’m currently an Applied Scientist at Amazon, where I lead the research on Amazon’s first production-ready virtual try-on model, focusing on image conditioned diffusion models. Previously, I completed multiple research internships at Google and Amazon during the summers of 2020-2024, where I worked on a range of projects, from self-supervised learning to diffusion models. Prior to my PhD, I worked at a tech company in Turkey for two years as a machine learning researcher on various projects on vision and language. mehmetsayginseyfioglu[at]gmail[dot]com |

|
|
My research interests revolve around self-supervised learning at the intersection of vision and language, visual instruction tuning, and generative diffusion models. |
|
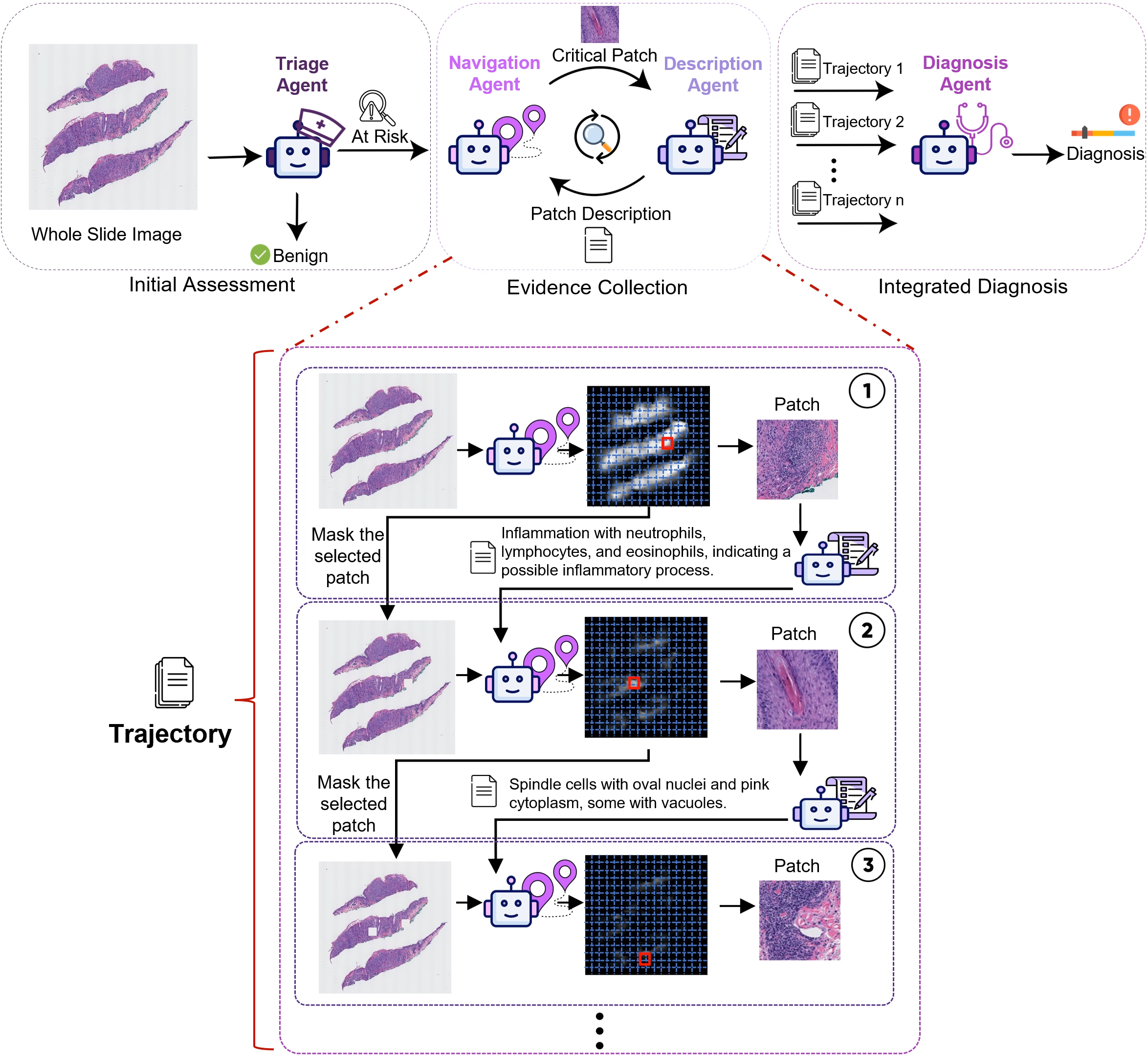
Mehmet Saygin Seyfioglu*, Fatemeh Ghezloo*, Rustin Soraki*, Wisdom O. Ikezogwo*, Beibin Li*, Tejoram Vivekanandan, Joann G. Elmore, Ranjay Krishna, Linda Shapiro ICCV 2025 Summary: Diagnosing diseases through histopathology whole slide images (WSIs) is fundamental in modern pathology but is challenged by the gigapixel scale and complexity of WSIs. PathFinder is a multi-modal, multi-agent framework that emulates the decision-making process of expert pathologists by integrating four AI agents: Triage, Navigation, Description, and Diagnosis. The Triage Agent distinguishes benign versus risky WSIs, then the Navigation and Description Agents collaboratively identify significant regions, provide importance maps, and generate natural language descriptions of relevant patches. Finally, the Diagnosis Agent synthesizes these findings into a comprehensive diagnosis. PathFinder outperforms state-of-the-art methods in skin melanoma diagnosis by 8% while offering inherent explainability, with pathologist evaluations finding that the descriptions it generates are on par with GPT-4. Remarkably, PathFinder is also the first AI system to surpass the average performance of pathologists on this task by 9%, setting a new standard for accurate and interpretable AI-assisted diagnostics in pathology. |
|
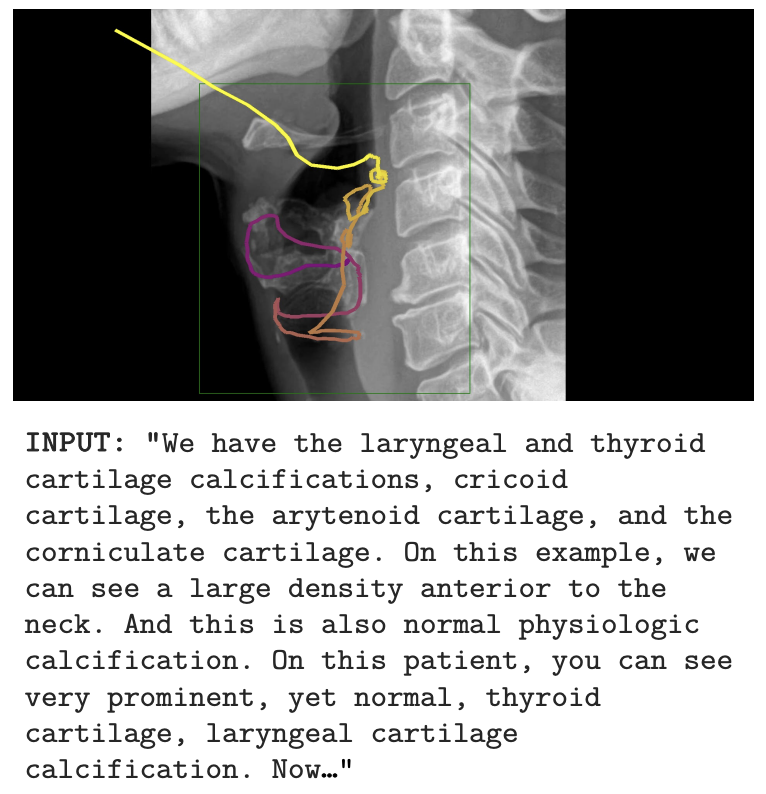
Wisdom O. Ikezogwo*, Kevin Zhang*, Mehmet Saygin Seyfioglu, Fatemeh Ghezloo, Ranjay Krishna, Linda Shapiro Neurips 2025 Summary: We propose MedicalNarratives, a dataset curated from medical pedagogical videos, inspired by Localized Narratives. It synchronizes instructors’ speech and mouse movements to create multimodal data for both semantic and dense objectives in medical AI tasks. MedicalNarratives contains 4.7M image-text pairs, with 1M having trace-level or bounding-box-level annotations. Trained with these data, our GenMedCLIP achieves state-of-the-art performance on medical imaging benchmarks spanning 12 domains, enabling integrated semantic and dense objectives without relying on separately trained models. |

|
Mehmet Saygin Seyfioglu, K. Bouyarmane, S. Kumar, A. Tavanaei and I. Tutar PrePrint January 2024. Summary: In e-commerce, a common challenge faced during virtual try-ons with zero-shot, image-conditioned inpainting models is their inability to preserve the fine-grained details of products. While frameworks like DreamPaint offer better quality, they rely on few-shot fine-tuning for each individual product, which is too costly. In this work, we introduce Diffuse2Choose, which enables any e-commerce product to be virtually placed in any user setting by preserving the product's fine-grained details in a zero-shot setting. It works by stitching the reference product directly into the source image to approximate its pixel-level appearance. A secondary UNet encoder then processes this collage, generating pixel-level signals. These signals are then modulated to the main UNet decoder through affine transformations using a FILM layer, ensuring high fidelity in detail preservation. In comparative evaluations, Diffuse2Choose outperforms both few-shot personalization models like DreamPaint and zero-shot inpainting models like Paint by Example, demonstrating superior results in both public virtual try-on datasets and in-house virtual try-all datasets. |

|
Mehmet Saygin Seyfioglu*, W. O. Ikezogwo*, F. Ghezloo*, R. Krishna and L. Shapiro CVPR 2024. Summary: We introduce Quilt-Instruct, a dataset with over 107,000 histopathology-specific instructional question/answer pairs, which we compiled from educational histopathology videos on YouTube, capturing narrators' cursor movements for spatial localization of captions. We distill key facts and diagnoses from the broader video content, leveraging these in GPT-4 prompts for contextually anchored, extrapolative reasoning, which helps minimize hallucinations when generating instruction tuning dataset. Quilt-Instruct led to the development of Quilt-LLaVA, a multi modal chatbot that excels in diagnostic reasoning and spatial awareness by reasoning beyond single image patches. Quilt-LLaVA shows a significant improvement over SOTA by over 10% on relative GPT-4 score and 4% and 9% on open and closed set VQA tasks. |
|
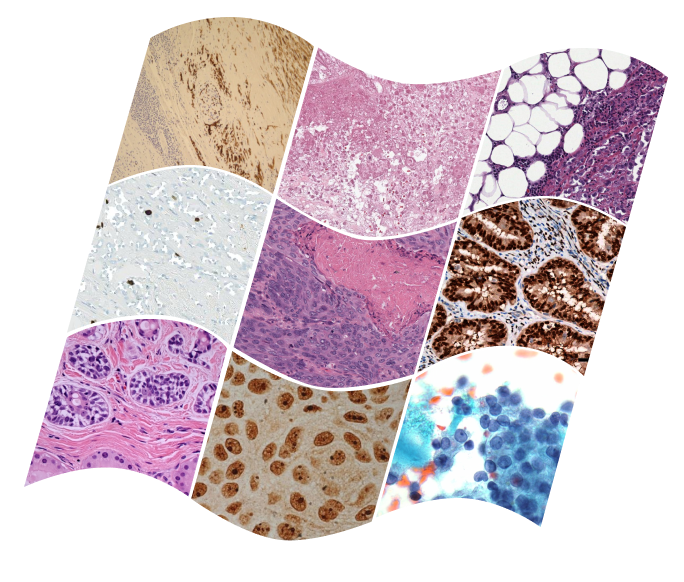
Mehmet Saygin Seyfioglu*, W. O. Ikezogwo*, F. Ghezloo*, D. Geva, F. S. Mohammed, P. K. Anand, R. Krishna and L. Shapiro NeurIPS ORAL 2023. Summary: We introduce Quilt-1M, the largest to date vision-language dataset created to aid representation learning in histopathology, utilizing various resources including YouTube. The dataset, assembled using a blend of handcrafted models and tools like large language models and automatic speech recognition, expands upon existing datasets by integrating additional data from sources like Twitter and research papers. A pre-trained CLIP model fine-tuned with Quilt-1M significantly outperforms state-of-the-art models for classifying histopathology images across 13 benchmarks spanning 8 sub-pathologies. |

|
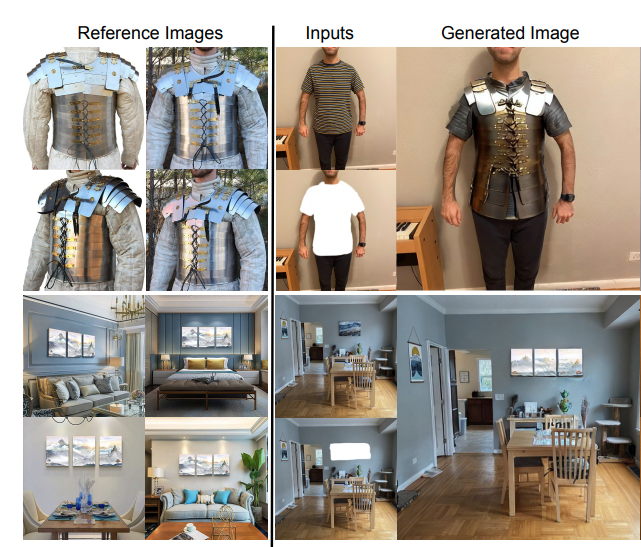
Mehmet Saygin Seyfioglu, K. Bouyarmane, S. Kumar, A. Tavanaei and I. B. Tutar PrePrint May 2023. Summary: DreamPaint is a framework for inpainting of e-commerce products onto user-provided context images, using only 2D images from product catalogs and user context. It utilizes few-shot fine-tuning of pre-trained diffusion models, allowing for accurate placement of products in images, preserving both product and context characteristics. DreamPaint outperforms state of the art inpainting modules in both subjective human studies and quantitative metrics, showcasing its potential for virtual try-ons in e-commerce. |
|
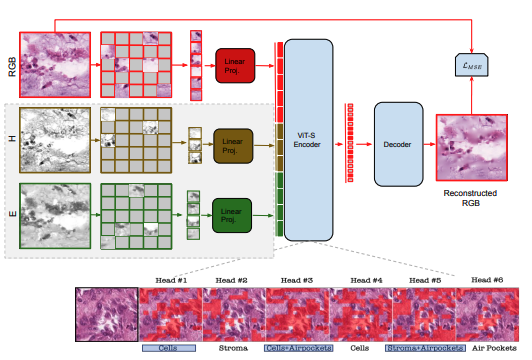
Mehmet Saygin Seyfioglu*, W.O. Ikezogwo*, and L. Shapiro Extended abstract: Machine Learning for Health (ML4H), Dec 2022. Summary: We propose the use of Multi-modal Masked Autoencoders (MMAE) in histopathology for self-supervised learning (SSL) on whole slide images. MMAE, utilizing specific compositionality of Hematoxylin & Eosin stained WSIs, shows superior performance over other state-of-the-art SSL techniques and supervised baselines in an eight-class tissue phenotyping task. |
|
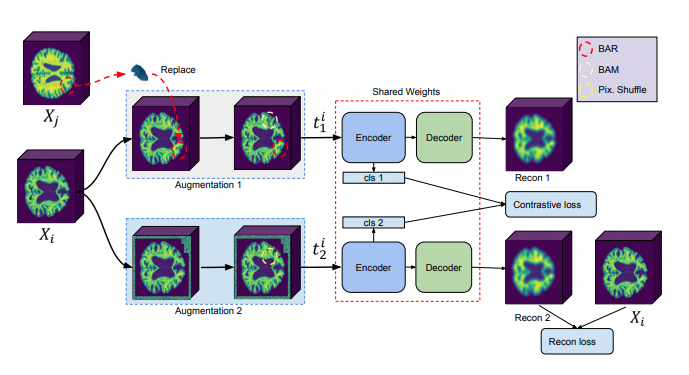
Mehmet Saygin Seyfioglu, Z. Liu, P. Kamath, S. Gangolli, S. Wang, T. Grabowski, and L. Shapiro MICCAI (Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention), 2022. Summary: We introduce a novel framework for Alzheimer's disease detection using brain MRIs. We utilize a data augmentation method called Brain-Aware Replacements (BAR) to generate synthetic samples. Then we trained a soft-label-capable supervised contrastive loss which aims to learn the relative similarity of representations. Through fine-tuning, the model pre-trained with this framework exhibits superior performance in the Alzheimer's disease detection task, outperforming other training approaches. |
|
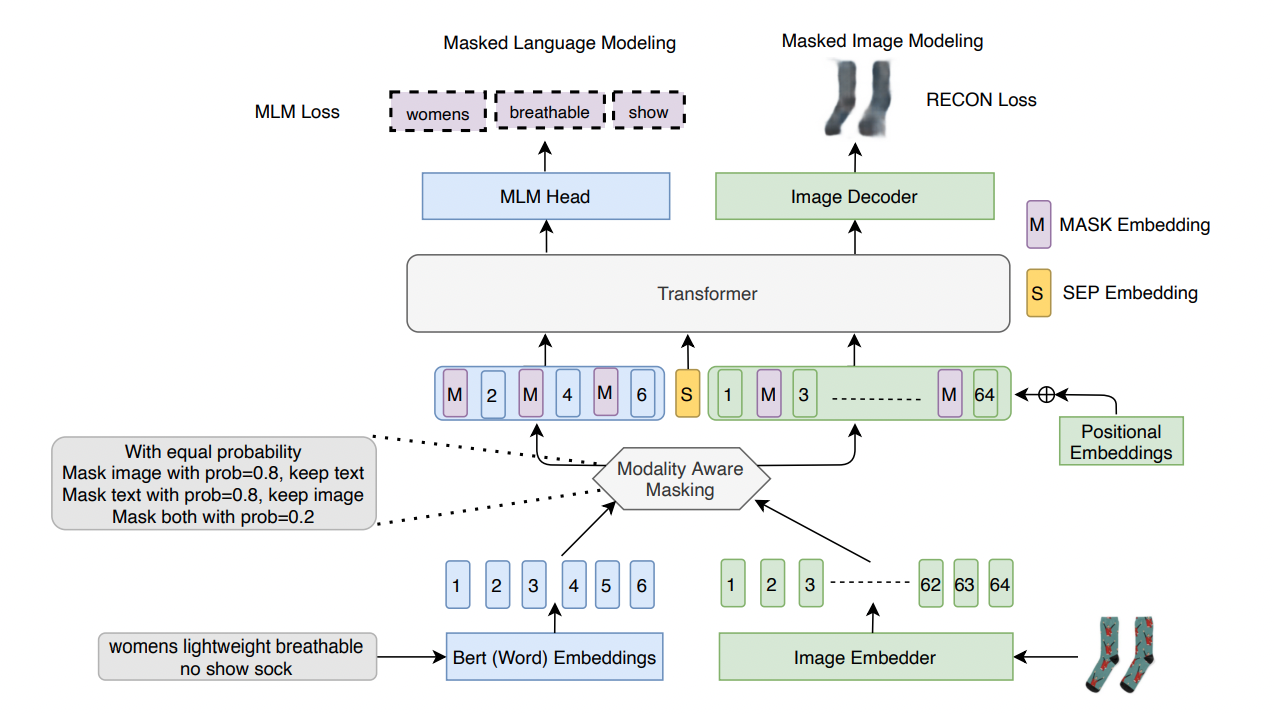
Mehmet Saygin Seyfioglu*, T. Arici*, T. Neiman, Y. Xu, S. Tran, T. Cilimbi, B. Zeng, and I. B. Tutar Preprint September 2021. Summary: We introduce Masked Language and Image Modeling for enhancing Vision-and-Language Pre-training by merging Masked Language Modeling (MLM) and reconstruction (Recon) losses. We also propose Modality Aware Masking (MAM) which aims to boost cross-modality interaction and separately gauge text and image reconstruction quality. By coupling MLM + Recon tasks with MAM, we exhibit a simplified VLP methodology, demonstrating improved performance on downstream tasks within a proprietary e-commerce multi-modal dataset. |
|
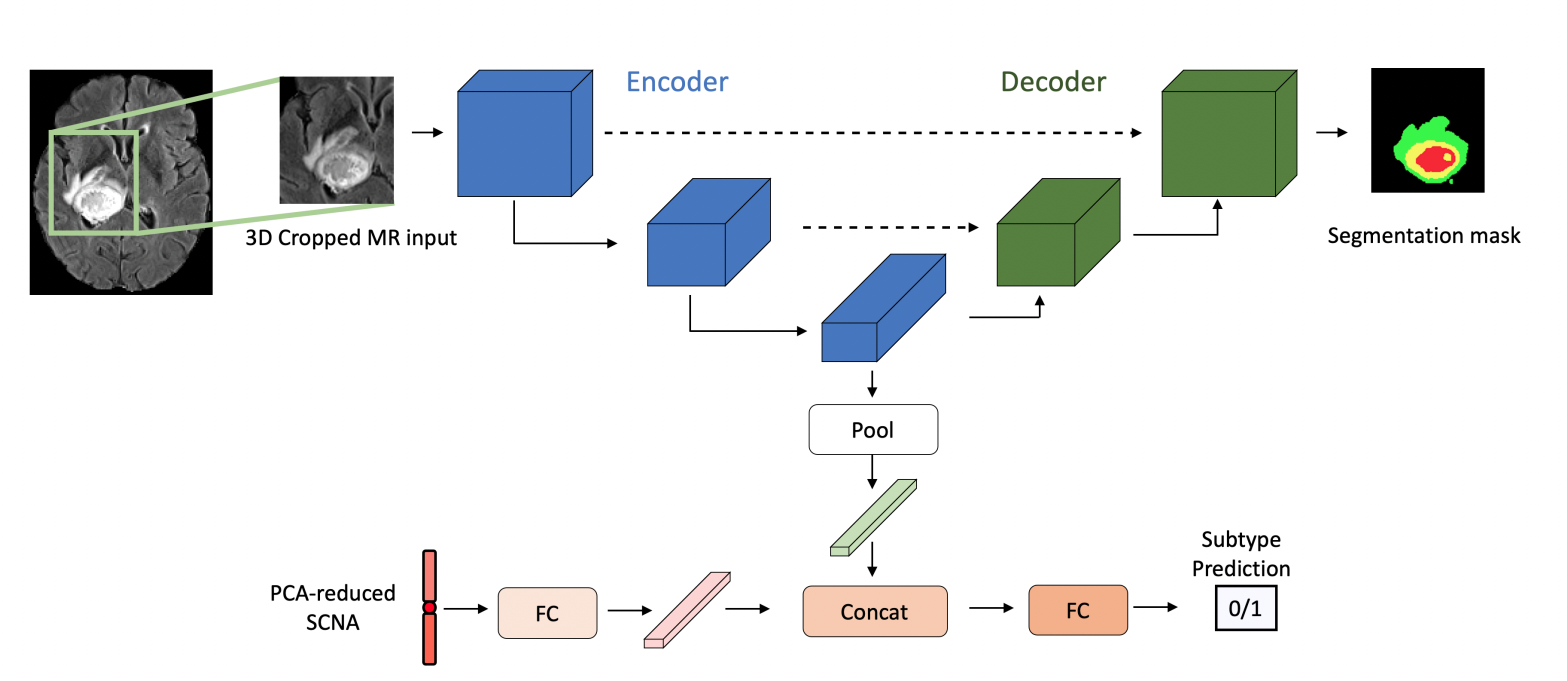
N. Nuechterlein, B. Li, Mehmet Saygin Seyfioglu, M. S. Seyfioğlu, S. Mehta, P. J. Cimino, and L. Shapiro ICPR May 2020. Summary: We address radio-genomic challenges in glioma subtype and survival prediction by utilizing multi-task learning (MTL) to leverage unlabeled MR data and combine it with genomic data. Our MTL model significantly surpasses comparable models trained only on labeled MR data for glioma subtype prediction tasks. We also demonstrate that our model's embeddings enhance survival predictions beyond using MR or somatic copy number alteration data alone. Our methodology showcases the potential of MTL in harnessing multimodal data for improved glioma characterization and survival prediction. |
|
I have some publications from my earlier work. Please see my Google Scholar page to see them. |
|
|

|
{TA} CSE 576: Computer Vision, Spring 2023.
{TA} CSE 473: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence, Winter/Fall 2023.
|
|
|